linux常用命令(一)
- sz、rz 下载上传
- 1. 安装:lrzsz
- 2. SecureCRT设置默认上传下载路径
- 3. rz
- 4. sz hello.txt
- mkdir创建目录
- tree
- touch
- vi & vim
- 1. 基础操作
- 2. :set nu 显示行号
- 3. gg 定位到某一行
- 4. / 查找,n下一处匹配
- 5. yy、p复制粘贴某一行
- 6. dd删除某一行
- 7. u 撤销(vim下撤销无限次)
- echo
- 1. > 重定向
- 2. >> 追加
- 3. 示例
- ls
- 1. ls -l 列出详细信息
- 2. ls -R -l 递归列出所有文件
- 3. ls -R -lts 递归列出并按更新时间排序
- 4. ls -F 区分文件类型
- cat
- 1. cat a.txt
- 2. cat >> a.txt << EOF
- pwd
- cp
- 1. cp 2.txt 2-copy.txt
- 2. cp -p 2.txt 2.txt.bak
- 3. cp -r asd asd.bak
- 4. cp -a asd asd.bak
- mv
- 常用
- 复制目录下所有文件及目录到
- rm
- 1. rm -r
- 2. rm –rf test
- head
- 1. head -c 4k f2 按大小输出
- 2. head -n 2 f2 按行输出
- tail
- 3. -c 按大小同head -c
- 4. -n 按行数同head -n
- 5. -f 即时输出文件变化
sz、rz 下载上传
上传下载命令,secureCRT中使用
1. 安装:lrzsz
|
[root@master ~]# yum install lrzsz ... Is this ok [y/N]: y ... Complete! |
2. SecureCRT设置默认上传下载路径
打开SecureCRT软件 -> Options -> session options -> X/Y/Zmodem 下可以设置上传和下载的目录。

3. rz
rz 的意思是:ZMODEM (Batch) file Receive,文件接收,相对于客户端来说就是上传文件。
|
rz waiting to receive. zmodem trl+C ȡ 100% 32 bytes 32 bytes/s 00:00:01 0 Errors |
4. sz hello.txt
Sz的意思是ZMODEM file send,文件发送,相对于客户端来说就是下载。
|
[root@master test]# sz hello.txt rz zmodem trl+C ȡ 100% 4 bytes 4 bytes/s 00:00:01 0 Errors [root@master test]# |
下载成功:
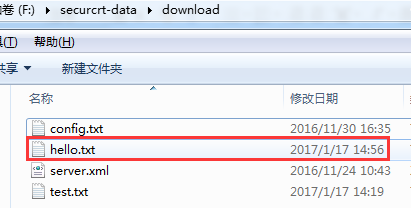
mkdir创建目录
mkdir - make directories
mkdir -p, --parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed
|
[root@master test]# mkdir a [root@master test]# ls a asdf.txt hello.txt test.txt [root@master test]# mkdir b/c mkdir: 无法创建目录"b/c": 没有那个文件或目录 [root@master test]# mkdir -p b/c [root@master test]# ls a asdf.txt b hello.txt test.txt [root@master test]# tree . ├── a ├── asdf.txt ├── b │ └── c ├── hello.txt └── test.txt |
tree
tree - list contents of directories in a tree-like format.
-i Don't print indentation lines.不以阶梯状显示。
-d List directories only.
-f Print the full path prefix for each file.显示完整的相对路径。
-s Print the size in bytes of each file.以字节显示大小。
-h Print the size in a more human readable way.以K、M单位显示大小,更人性化。
-t Sort files by last modification time.按时间排序。
-I<范本样式> Do not list files that match the given pattern.不显示匹配的
-P<范本样式> List only those files that match the pattern given.只显匹配的
-D Print the date of last modification.显示更改时间。
-p Print the protections for each file.列出权限标示。
-v Sort files alphanumerically by version. 按名称升序排序
-r Sort files in reverse alphanumeric order.按名称降序排序
-l Follow symbolic links like directories.如遇到性质为符号连接的目录,直接列出该连接所指向的原始目录。
-g Displays file group owner or GID number.列出文件或目录的所属群组名称,没有对应的名称时,则显示群组识别码。
|
[root@master test]# tree . ├── a ├── asdf.txt ├── b │ └── c ├── c │ └── a │ └── b │ ├── a.txt │ ├── b.txt │ ├── c.log │ └── c.txt ├── hello.txt └── test.txt |
|
[root@master test]# tree -P "*.txt" . ├── a ├── asdf.txt ├── b │ └── c ├── c │ └── a │ └── b │ ├── a.txt │ ├── b.txt │ └── c.txt ├── hello.txt └── test.txt |
|
[root@master test]# tree -L 2 -P "*.txt" . ├── a ├── asdf.txt ├── b │ └── c ├── c │ └── a ├── hello.txt └── test.tx |
|
[root@master test]# tree -fsti . [ 37] ./asdf.txt [ 4096] ./c [ 4096] ./c/a [ 4096] ./c/a/b [ 11] ./c/a/b/c.log [ 11] ./c/a/b/c.txt [ 11] ./c/a/b/b.txt [ 11] ./c/a/b/a.txt [ 4096] ./b [ 4096] ./b/c [ 4096] ./a [ 4] ./hello.txt [ 4] ./test.txt |
touch
Update the access and modification times of each FILE to the current time.
A FILE argument that does not exist is created empty, unless -c or -h is supplied.
-a change only the access time
-c no-create do not create any files
-m change only the modification time
|
[root@master test]# touch toucht.txt [root@master test]# ls -ld toucht.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 17 17:43 toucht.txt [root@master test]# touch toucht.txt [root@master test]# ls -ld toucht.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 0 1月 17 17:44 toucht.txt [root@master test]# |
vi & vim
1. 基础操作
记事本编辑器,执行vi hello.txt进入vi编辑器,点击a或i进入编辑模式,编辑完成后按esc键退出编辑模式进入到命令模式,最后:wq保存退出,wq-->write quit。
:wq 保存文件并退出vi
:q! 不保存文件,强制退出vi
:w 保存文件但不退出vi
:w file 将修改另外保存到file中,不退出vi
:w! 强制保存,不推出vi
:wq! 强制保存文件,并退出vi
q: 不保存文件,退出vi
:e! 放弃所有修改,从上次保存文件开始再编辑
|
[root@master test]# vi hello.txt 1 123 2 ni hao 3 hah 4 sdf |
2. :set nu 显示行号
|
15 sdf 16 sdf 17 sdnif 18 sdf 19 sdf 20 sdf :set nu |
3. gg 定位到某一行
查看模式下,输入行号,按gg定位到某一行
4. / 查找,n下一处匹配
|
17 sdnif 18 sdf 19 sdf 20 sdf 21 sdf /ni |
5. yy、p复制粘贴某一行
yy复制当前行,p粘贴
6. dd删除某一行
7. u 撤销(vim下撤销无限次)
echo
echo 打印输出内容
1. > 重定向
echo xxx > file 覆盖内容到文件 文件不存在则创建
2. >> 追加
echo xxxx >> file 追加内容到文件 文件不存在则创建
3. 示例
|
[root@master test]# echo 1123 1123 [root@master test]# ls a asdf.txt b c hello.txt tch.txt test.txt toucht.txt [root@master test]# echo 234234asdfasd > 2323.txt [root@master test]# ls 2323.txt a asdf.txt b c hello.txt tch.txt test.txt toucht.txt [root@master test]# cat 2323.txt 234234asdfasd [root@master test]# echo 234234 > 2323.txt [root@master test]# cat 2323.txt 234234 [root@master test]# echo asdfasd >> 2323.txt [root@master test]# cat 2323.txt 234234 asdfasd [root@master test]# |
ls
列出文件列表
-l 列出文件的详细信息,如创建者,创建时间,文件的读写权限列表等等。
-R 将目录下所有的子目录的文件都列出来,相当于我们编程中的“递归”实现
-s 在每个文件的后面打印出文件的大小。
-t 按时间进行文件的排序 Time(时间)
-S 以文件的大小进行排序
-F 区分文件类型
-h 人性化显示大小human 与 tree中的-h一样
-i 文件的索引号inode
1. ls -l 列出详细信息
|
[root@master a]# ls a.txt b [root@master a]# ls -l 总用量 8 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4 1月 18 17:24 a.txt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 1月 17 15:25 b |
2. ls -R -l 递归列出所有文件
|
[root@master a]# ls -R -l .: 总用量 8 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4 1月 18 17:24 a.txt drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 1月 17 15:25 b ./b: 总用量 16 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:24 a.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:24 b.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:25 c.log -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:24 c.txt |
3. ls -R -lts 递归列出并按更新时间排序
|
[root@master a]# ls -R -lst .: 总用量 8 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 4 1月 18 17:24 a.txt 4 drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 1月 17 15:25 b ./b: 总用量 16 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:25 c.log 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:24 c.txt 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:24 b.txt 4 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 11 1月 17 15:24 a.txt [root@master a]# |
4. ls -F 区分文件类型
|
[root@localhost test]# ls -F a.tar a.txt dir/ [root@localhost test]# |
cat
1. cat a.txt
查看文档内容
|
[root@master test]# cat a.txt 123 1233 asdfasd |
2. cat >> a.txt << EOF
EOF只是输入开始标志,任何字符都可以,必须跟结束标志一致才能退出并保存。当a.txt不存在的时候,自动创建文件。
|
[root@master test]# cat >> a.txt << EOF > new hello > EOF [root@master test]# cat a.txt 123 1233 asdfasd new hello |
pwd
pwd - print name of current/working directory查看当前目录路径
|
[root@master test]# pwd /root/test |
cp
cp - copy files and directories
1. cp 2.txt 2-copy.txt
|
[root@master test]# cp 2323.txt 2323-copy.txt [root@master test]# ls -l 总用量 32 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 15 1月 19 09:20 2323-copy.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 15 1月 18 16:40 2323.txt |
2. cp -p 2.txt 2.txt.bak
连同档案的属性一起复制。
|
[root@master test]# cp -p 2323.txt 2323.txt.bak cp:是否覆盖"2323.txt.bak"? y [root@master test]# ll 总用量 36 -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 15 1月 18 16:40 2323.txt -rw-r--r--. 1 root root 15 1月 18 16:40 2323.txt.bak |
3. cp -r asd asd.bak
-R, -r, --recursive 递归拷贝,用于拷贝目录
|
[root@master test]# tree -D asd asd └── [Jan 19 9:22] a ├── [Jan 19 9:22] a.txt └── [Jan 19 9:22] b ├── [Jan 19 9:22] a.txt ├── [Jan 19 9:22] b.txt ├── [Jan 19 9:22] c.log └── [Jan 19 9:22] c.txt [root@master test]# cp asd asd.bak cp: 略过目录"asd" [root@master test]# cp -r asd asd.bak [root@master test]# tree -D asd.bak/ asd.bak/ └── [Jan 19 14:18] a ├── [Jan 19 14:18] a.txt └── [Jan 19 14:18] b ├── [Jan 19 14:18] a.txt ├── [Jan 19 14:18] b.txt ├── [Jan 19 14:18] c.log └── [Jan 19 14:18] c.txt |
4. cp -a asd asd.bak
Copy SOURCE to DEST, or multiple SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY.
-a same as -dR --preserve=all相当于 - pdr,保持文档原有属性递归拷贝。
|
[root@master test]# cp -a asd asd.bak [root@master test]# tree -D asd.bak/ asd.bak/ ├── [Jan 19 14:18] a │ ├── [Jan 19 14:18] a.txt │ └── [Jan 19 14:18] b │ ├── [Jan 19 14:18] a.txt │ ├── [Jan 19 14:18] b.txt │ ├── [Jan 19 14:18] c.log │ └── [Jan 19 14:18] c.txt └── [Jan 19 9:22] asd └── [Jan 19 9:22] a ├── [Jan 19 9:22] a.txt └── [Jan 19 9:22] b ├── [Jan 19 9:22] a.txt ├── [Jan 19 9:22] b.txt ├── [Jan 19 9:22] c.log └── [Jan 19 9:22] c.txt 5 directories, 10 files |
mv
常用
mv - move (rename) files移动文档目录、重命名等
f1、f2是文件,/d1,/d2是目录
mv f1 f2:如果f2不存在则f1重命名为f2;如果f2存在,则f1重命名为f2并覆盖f2。

复制目录下所有文件及目录到
把a目录连同a目录下面的所有东西拷贝到b
cp -r a/ b/
只会拷贝a目录下面的所有
cp -r a/* b/
rm
rm - remove files or directories
1. rm -r
-r, -R, --recursive 递归删除目录及其内容
2. rm –rf test
-f, --force 强制删除。忽略不存在的文件,不提示确认
|
[root@master ~]# rm test rm: 无法删除"test": 是一个目录 [root@master ~]# rm -f test rm: 无法删除"test": 是一个目录 [root@master ~]# rm -r test rm:是否进入目录"test"? n [root@master ~]# rm -rf test |
head
head - output the first part of files
法:head [选项]... [文件]...
将每个指定文件的头10 行显示到标准输出。
如果指定了多于一个文件,在每一段输出前会给出文件名作为文件头。
如果不指定文件,或者文件为"-",则从标准输入读取数据。
长选项必须使用的参数对于短选项时也是必需使用的。
-c, --bytes=[-]K 显示每个文件的前K 字节内容;
如果附加"-"参数,则除了每个文件的最后K字节数据外
显示剩余全部内容
-n, --lines=[-]K 显示每个文件的前K 行内容;
如果附加"-"参数,则除了每个文件的最后K 行外显示
剩余全部内容
1. head -c 4k f2 按大小输出
--bytes=[-]K print the first K bytes of each file; with the leading ‘-’, print all but the last K bytes of each file
|
[root@master test]# head -c 4k f2 asdfasd 23423 wer2e3 sdfg34 234 234zadfa23 3rxva asdfa asdfasd [root@master test]# head -c 4 f2 asdf[root@master test]# |
2. head -n 2 f2 按行输出
-n, --lines=[-]K print the first K lines instead of the first 10; with the leading ‘-’, print all but the last K lines of each file
|
[root@master test]# head -2 f2 asdfasd 23423 [root@master test]# head -n 2 f2 asdfasd 23423 |
tail
tail - output the last part of files
用法:tail [选项]... [文件]...
显示每个指定文件的最后10 行到标准输出。
若指定了多于一个文件,程序会在每段输出的开始添加相应文件名作为头。
如果不指定文件或文件为"-" ,则从标准输入读取数据。
3. -c 按大小同head -c
4. -n 按行数同head -n
5. -f 即时输出文件变化
-f, --follow[={name|descriptor}] 即时输出文件变化后追加的数据。-f, --follow 等于--follow=descriptor
可用于监听查看日志文件的实时输出内容。

按ctrl+c退出监听查看。退出不了,查看secureCRT的配置把CUA设置取消复制粘贴。
如图:

评论
发表评论
|
|
|